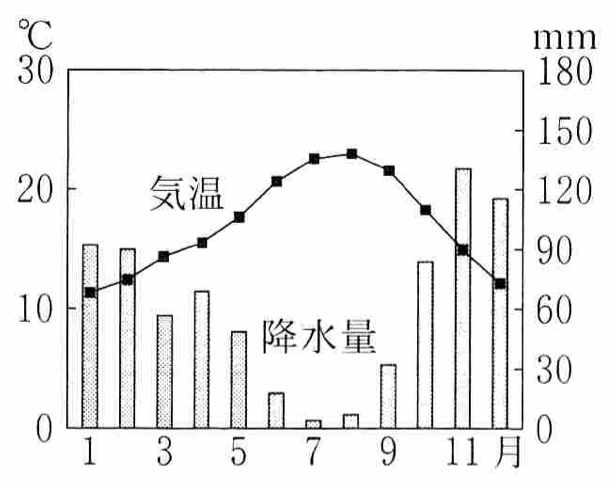
2021年の共通テスト「地理B」の問題より:

このようなグラフを雨温図と呼ぶらしい。
適当な地点の雨温図を描いてみよう。気象庁の過去の気象データ・ダウンロードから,データの種類は月別値,地点は石狩→札幌,項目は月平均気温と降水量の月合計,期間は2019年1月〜12月,表示オプションは適宜設定してCSVをダウンロードすると次のようになった:
ダウンロードした時刻:2021/01/23 09:51:03 ,,札幌,札幌,札幌,札幌,札幌 年,月,降水量の合計(mm),降水量の合計(mm),降水量の合計(mm),平均気温(℃),平均気温(℃) ,,,現象なし情報,均質番号,,均質番号 2019,1,86.0,0,1,-3.0,1 2019,2,32.5,0,1,-2.6,1 2019,3,39.0,0,1,2.5,1 2019,4,30.5,0,1,8.0,1 2019,5,29.5,0,1,15.7,1 2019,6,71.0,0,1,17.4,1 2019,7,31.5,0,1,21.7,1 2019,8,144.5,0,1,22.5,1 2019,9,108.5,0,1,19.3,1 2019,10,97.0,0,1,13.3,1 2019,11,82.0,0,1,3.9,1 2019,12,62.0,0,1,-0.8,1
最初の5行を無視して読む:
import pandas as pd
df = pd.read_csv("data.csv", skiprows=5, header=None, encoding="cp932")
0 1 2 3 4 5 6
0 2019 1 86.0 0 1 -3.0 1
1 2019 2 32.5 0 1 -2.6 1
2 2019 3 39.0 0 1 2.5 1
3 2019 4 30.5 0 1 8.0 1
4 2019 5 29.5 0 1 15.7 1
5 2019 6 71.0 0 1 17.4 1
6 2019 7 31.5 0 1 21.7 1
7 2019 8 144.5 0 1 22.5 1
8 2019 9 108.5 0 1 19.3 1
9 2019 10 97.0 0 1 13.3 1
10 2019 11 82.0 0 1 3.9 1
11 2019 12 62.0 0 1 -0.8 1
気温を折れ線グラフで表示する:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.plot(df[1], df[5], "o-")
plt.xlabel("月")
plt.ylabel("平均気温(℃)")
plt.bar(df[1], df[2])
plt.xlabel("月")
plt.ylabel("降水量(mm)")
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
ax2 = ax.twinx()
ax.plot(df[1], df[5], "o-", color="C1", linewidth=3)
ax2.bar(df[1], df[2])
plt.xticks(range(1, 13)) # 全部の月に番号を付ける
ax.patch.set_visible(False)
ax.set_zorder(1)
ax.set_xlabel("月")
ax.set_ylabel("平均気温(℃)")
ax2.set_ylabel("降水量(mm)")
ax.legend(['平均気温'], loc="upper left")
ax2.legend(['降水量'], loc="upper right")
Last modified: